Magnetic Encoding Type
- Home
- Magnetic Encoding Type
ISO (Default)
The encoder reads and writes standard ISO track data formats in standard ISO track locations. The following shows the three standard ISO track.
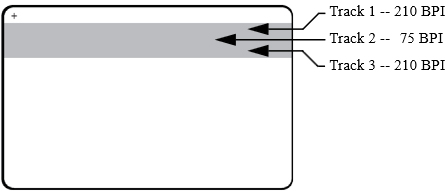
Each track can be encoded and decoded with ASCII characters in the standard default ISO data formats:
| Track | Density (bpi) | Bits per character | Character parity | Length (characters) | LRC parity | Start sentinel | End sentinel | Start sentinel offset |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 210 | 7 | Odd | 76 | Even | % | ? | 0.293″ (7.4 mm) |
| 2 | 75 | 5 | Odd | 37 | Even | ; | ? | 0.293″ (7.4 mm) |
| 3 | 210 | 5 | Odd | 104 | Even | ; | ? | 0.293″ (7.4 mm) |
The magnetic encoder can read or encode up to 3 tracks of digital information onto CR-80 cards incorporating a HiCo or LoCo magnetic stripe in the ISO 7811 format.
Encoding for the three tracks uses ISO 7811 format.
- Track 1 uses 210 BPI (bit per inch) encoding in the International Air Transport Association (IATA) format of 79 alphanumeric characters, at 7 bits per character.
- Track 2 uses 75 BPI to encoding to store 40 numeric characters at 5 bits per character in American Banking Association (ABA) format.
- Track 3 uses 210 BPI encoding of 107 numeric characters at 5 bits per character in THRIFT format.
The ISO data formats include a preamble (all zeros), a start character, data (7-bit or 5-bit as specified by ISO), a stop character, and a Longitudinal Redundancy Check (LRC) character. The 7-bit data format has 6 bits of encoded data and parity bit. The 5-bit data format has 4 bits of encoded data and a parity bit.
The ISO data format include a data field separator (or delimiter) that allows parsing of the encoded track data. An example of separate data fields would be the ABA data format (Track 2) that includes a Primary Account Number (PAN) field and an account information field (for expiration date, country code, etc.).
AAMVA
The data stored on magnetic stripes on American driver’s licenses is specified by the American Association of Motor Vehicle Administrators (AAMVA).
Alpha-numeric characters on Track 1 and 3, numerals only on Track 2.
| Track | Density (bpi) | Bits per character | Character parity | Length (characters) | LRC parity | Start sentinel | End sentinel | Start sentinel offset inches (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 210 | 7 | Odd | 79 | Even | % | ? | 0.293″ (7.4) |
| 2 | 75 | 5 | Odd | 37 | Even | ; | ? | 0.293″ (7.4) |
| 3 | 210 | 7 | Odd | 79 | Even | % | ? | 0.293″ (7.4) |
CUSTOM
If a custom format is desired, the ISO standard format may be used as a starting point. The standard format can then be modified by assigning different values to any or all of the density,
characters and sentinel attributes. (If any of these attributes is missing, its corresponding value in the standard ISO format will be substituted.).
BINARY
The binary option allows the user to specify directly the value for each each bit on the mag stripe:.
In this “direct binary ” mode, it is the host’s responsibility to fully populate the magnetic stripe;
i.e., the hex data provided by the host must include the leading zeroes, start sentinel, data, end sentinel, LRC, and trailing zeroes. Note that the magnetic stripe is encoded from the right-hand end as viewed from the “stripe“ side, with the stripe uppermost. The least significant bit of the data is encoded first.
A sufficient number of leading zeroes should be prepended to offset the start sentinel by approximately 0.3” (7.5 mm) from the right-hand end, as in the ISO format. Care should be taken to ensure that the payload data does not exceed the capacity of the tracks at their specified recording densities. (In the binary mode, out-of-range data is not recorded, and no error condition will result.).
A CR-80 size card has a nominal capacity of 252 bits per track at 75 BPI, and 708 bits at 210 BPI. These capacities equate approximately to 31 hex bytes (248 binary bits) and 88 hex bytes respectively.